3.4 Muscle Tissue and Motion
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify the three types of muscle tissue
- Compare and contrast the functions of each muscle tissue type
- Explain how muscle tissue can enable motion
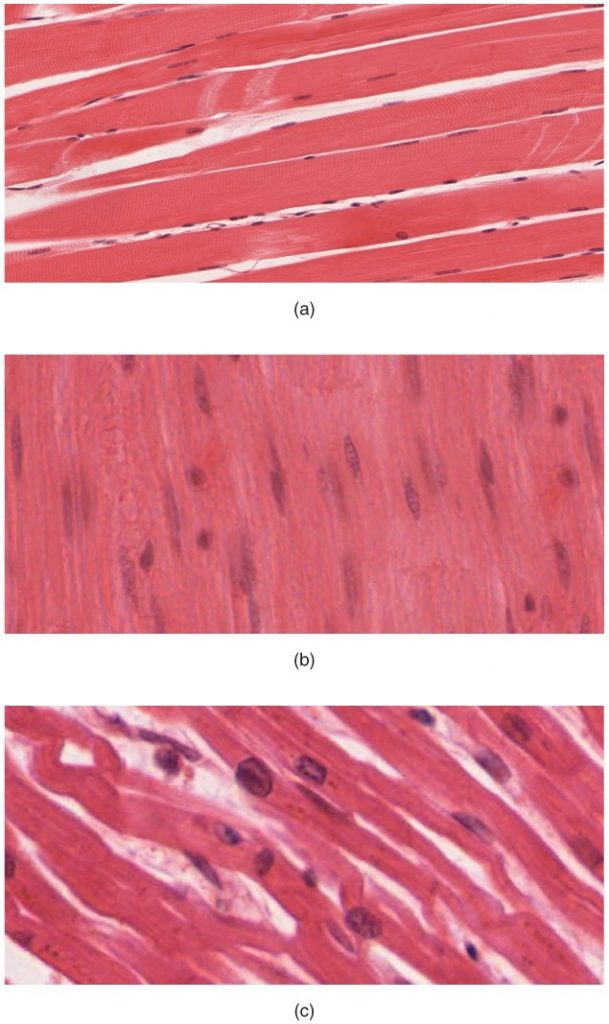
Muscle tissue is characterised by properties that allow movement. Muscle cells are excitable; they respond to a stimulus. They are contractile, meaning they can shorten and generate a pulling force. When attached between two movable objects, in other words, bones, contractions of the muscles cause the bones to move. Some muscle movement is voluntary, which means it is under conscious control. For example, a person decides to open a book and read a chapter on anatomy. Other movements are involuntary, meaning they are not under conscious control, such as the contraction of your pupil in bright light. Muscle tissue is classified into three types according to structure and function: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth (Table 3.4.1).
Table 3.4.1. Comparison of structure and properties of muscle tissue types
| Tissue | Histology | Function | Location |
| Skeletal | Long cylindrical fibre, striated, many peripherally located nuclei | Voluntary movement, produces heat, protects organs | Attached to bones and around entrance points to body (e.g., mouth, anus) |
| Cardiac | Short, branched, striated, single central nucleus | Contracts to pump blood | Heart |
| Smooth | Short, spindle-shaped, no evident striation, single nucleus in each fibre | Involuntary movement, moves food, involuntary control of respiration, moves secretions, regulates flow of blood in arteries by contraction | Walls of major organs and passage ways |
Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and its contraction makes possible locomotion, facial expressions, posture, and other voluntary movements of the body. Forty percent of your body mass is made up of skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscles generate heat as a by-product of their contraction and thus participate in thermal homeostasis. Shivering is an involuntary contraction of skeletal muscles in response to perceived lower than normal body temperature. The muscle cell, or myocyte, develops from myoblasts derived from the mesoderm. Myocytes and their numbers remain relatively constant throughout life. Skeletal muscle tissue is arranged in bundles surrounded by connective tissue. Under the light microscope, muscle cells appear striated with many nuclei squeezed along the membranes. The striation is due to the regular alternation of the contractile proteins, actin and myosin, along with the structural proteins that couple the contractile proteins to connective tissues. The cells are multinucleated as a result of the fusion of the many myoblasts that fuse to form each long muscle fibre.
Cardiac muscle forms the contractile walls of the heart. The cells of cardiac muscle, known as cardiomyocytes, also appear striated under the microscope. Unlike skeletal muscle fibres, cardiomyocytes are single cells typically with a single centrally located nucleus. A principal characteristic of cardiomyocytes is that they contract on their own intrinsic rhythms without any external stimulation. Cardiomyocyte attach to one another with specialised cell junctions called intercalated discs. Intercalated discs have both anchoring junctions and gap junctions. Attached cells form long, branching cardiac muscle fibres that are, essentially, a mechanical and electrochemical syncytium allowing the cells to synchronise their actions. The cardiac muscle pumps blood through the body and is under involuntary control. The attachment junctions hold adjacent cells together across the dynamic pressures changes of the cardiac cycle.
Smooth muscle tissue contraction is responsible for involuntary movements in the internal organs. It forms the contractile component of the digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems as well as the airways and arteries. Each cell is spindle shaped with a single nucleus and no visible striations (Figure 3.4.1).
Section Review
The three types of muscle cells are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Their morphologies match their specific functions in the body. Skeletal muscle is voluntary and responds to conscious stimuli. The cells are striated and multinucleated appearing as long, unbranched cylinders. Cardiac muscle is involuntary and found only in the heart. Each cell is striated with a single nucleus and they attach to one another to form long fibres. Cells are attached to one another at intercalated disks. The cells are interconnected physically and electrochemically to act as a syncytium. Cardiac muscle cells contract autonomously and involuntarily. Smooth muscle is involuntary. Each cell is a spindle-shaped fibre and contains a single nucleus. No striations are evident because the actin and myosin filaments do not align in the cytoplasm.
Review Questions
Critical Thing Questions
Click the drop down below to review the terms learned from this chapter.

