3 Body Cavities and Serous Membranes
The body maintains its internal organisation by means of membranes, sheaths, and other structures that separate compartments. The dorsal (posterior) cavity and the ventral (anterior) cavity are the largest body compartments (Figure 1.11). These cavities contain and protect delicate internal organs and the ventral cavity allows for significant changes in the size and shape of the organs as they perform their functions. The lungs, heart, stomach and intestines, for example, can expand and contract without distorting other tissues or disrupting the activity of nearby organs.
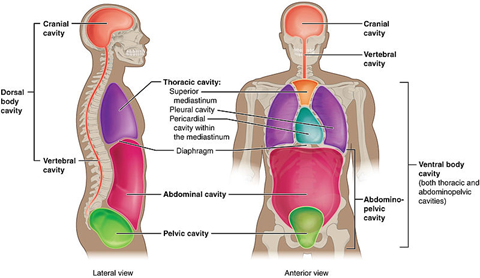
Subdivisions of the Posterior (Dorsal) and Anterior (Ventral) Cavities
The posterior (dorsal) and anterior (ventral) cavities are each subdivided into smaller cavities. In the posterior (dorsal) cavity, the cranial cavity houses the brain and the spinal cavity (or vertebral cavity) encloses the spinal cord. Just as the brain and spinal cord make up a continuous, uninterrupted structure, the cranial and spinal cavities that house them are also continuous. The brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column and by cerebrospinal fluid, a colourless fluid produced by the brain, which cushions the brain and spinal cord within the posterior (dorsal) cavity.
The anterior (ventral) cavity has two main subdivisions: the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity (see Figure 1.12). The thoracic cavity is the more superior subdivision of the anterior cavity, and it is enclosed by the rib cage. The thoracic cavity contains the lungs and the heart, which is located in the mediastinum. The diaphragm forms the floor of the thoracic cavity and separates it from the more inferior abdominopelvic cavity. The abdominopelvic cavity is the largest cavity in the body. Although no membrane physically divides the abdominopelvic cavity, it can be useful to distinguish between the abdominal cavity, the division that houses the digestive organs, and the pelvic cavity, the division that houses the organs of reproduction.
Towards the back of the body.
Towards the front of the body.
In behind or behind.
In front of or front.
Interior space of the skull that houses the brain.
Division of the dorsal cavity that houses the spinal cord; also referred to as vertebral cavity.
Division of the anterior (ventral) cavity that houses the heart, lungs, oseophagus and trachea.
Division of the anterior (ventral) cavity that houses the abdominal and pelvic viscera.

